Navdeep Gill works at the intersection of Responsible AI, AI Governance, and AI Risk Management, developing strategies and solutions that ensure AI systems meet the highest standards of transparency, fairness, accountability, and robustness. Currently, at ServiceNow, he collaborates with cross-functional teams to operationalize AI policies and risk frameworks, helping scale responsible AI practices across enterprise applications.
During his time at H2O.ai, Navdeep contributed to a wide range of initiatives spanning machine learning interpretability, automated machine learning (AutoML), and GPU-accelerated model training. He played a key role in embedding interpretability into H2O’s flagship AutoML platform, Driverless.ai, and was instrumental in the development of H2O AutoML, H2O4GPU, and H2O-3—projects that advanced distributed and accelerated machine learning for industry-scale data science.
In earlier work at Scry AI and FICO, Navdeep designed and deployed machine learning and analytics solutions across financial services, telecommunications, and market research.
Before entering the tech industry, Navdeep conducted research in cognitive neuroscience and visual psychophysics. At the University of California, San Francisco, he studied neural mechanisms of memory and attention, focusing on how these functions change with aging and dementia. At the Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute, he explored how the brain perceives depth in 3D space, with a focus on the effects of brain injuries on visual perception and eye movement control.
Education

California State University, East Bay
Hayward, CA
M.S. in Statistics with Designated Emphasis in Computational Statistics
Graduated 2014
B.S. in Statistics; B.A. in Psychology; Minor in Mathematics
Graduated 2012
Industry Experience

ServiceNow
Santa Clara, CA
Staff Senior Product Manager - Responsible AI
2024 - present

H2O.ai
Mountain View, CA
Manager, Lead Data Scienist
2021 - 2024
Senior Software Engineer
2018 - 2021
Software Engineer
2015 - 2018

Scry AI
San Jose, CA
Senior Research Analyst
2014 - 2015

FICO
San Rafael, CA
Analytic Science Consultant
2013 - 2014
Academic Experience

University of California, San Francisco
San Francisco, CA
Research Intern
2012

Smith Kettlewell Eye Research Institute
San Francisco, CA
Research Intern
2011
Projects
Current:
- Responsible AI at ServiceNow - Responsible AI initiatives at ServiceNow
Past:
- Responsible AI at H2O.ai - Responsible AI initiatives at H2O.ai
- AI Governance at H2O.ai - AI Governance initiatives at H2O.ai
- Driverless AI - H2O.ai's flagship automatic machine learning platform
- H2O Model Security - Evaluate and analyze the security of H2O Driverless AI models
- H2O-3 - H2O.ai's open source, in-memory, distributed, and scalable machine learning and predictive analytics platform
- H2O AutoML - H2O.ai's AutoML platform
- H2O4GPU - H2O.ai's GPU-accelerated machine learning package with APIs in Python and R
- rsparkling - R interface for H2O Sparkling Water, combining H2O-3's machine learning algorithms with Apache Spark
Presentations
Publications
- Gill, N., Zhang, S. (2023). Guidelines for Effective AI Governance with Applications in H2O AI Cloud. H2O.ai.
- Gill, N., Mathur, A., Conde, M. (2022). A Brief Overview of AI Governance in Responsible Machine Learning Systems. In NeurIPS Workshop on Trustworthy and Socially Responsible Machine Learning (TSRML).
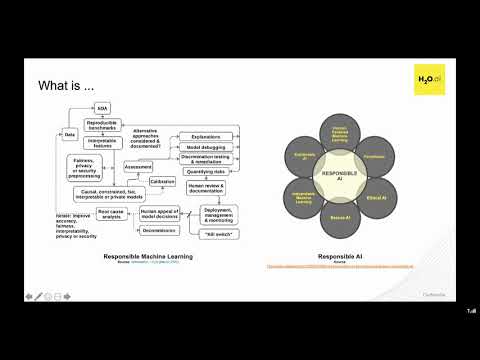
- Hall, P., Gill, N., Cox, B. (2020). Responsible Machine Learning: Actionable Strategies for Mitigating Risk and Driving Adoption. Sebastopol, CA, USA: O’Reilly Media, Inc.
- Gill, N., Hall, P., Montgomery, K., Schmidt, N. (2020). A Responsible Machine Learning Workflow with Focus on Interpretable Models, Post-hoc Explanation, and Discrimination Testing. Information, 11(3):137.
- Hall, P., Gill, N. (2019). An Introduction to Machine Learning Interpretability, Second Edition: An Applied Perspective on Fairness, Accountability, Transparency, and Explainable AI. Sebastopol, CA, USA: O’Reilly Media, Inc.
- Hall, P., Gill, N., Schmidt, N. (2019). Proposed Guidelines for the Responsible Use of Explainable Machine Learning. In NeurIPS Workshop on Robust AI in Financial Services.
- Hall, P., Gill, N., Meng, L. (2018). Testing Machine Learning Explanation Techniques. Newton, MA, USA: O’Reilly Media.
- Hall, P., Gill, N. (2018). An Introduction to Machine Learning Interpretability: An Applied Perspective on Fairness, Accountability, Transparency, and Explainable AI. Newton, MA, USA: O’Reilly Media, Inc.
- Hall, P., Gill, N., Kurka, M., Phan, W. (2017). Machine Learning Interpretability with H2O Driverless AI. H2O.ai.
- Voytek, B., Samaha, J., Rolle, C. E., Greenberg, Z., Gill, N., Porat, S. (2017). Preparatory Encoding of the Fine Scale of Human Spatial Attention. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 29, 1302–1310.
- Tyler, C.W., Elsaid, A.M., Likova, L.T., Gill, N., & Nicholas, S.C. (2012). Analysis of Human Vergence Dynamics. Journal of Vision, 12(11):21; doi:10.1167/12.11.21.
Conference Presentations
- Mohammadi, K., Puri, A., Belanger Albarran, G., Bansal, M., Gill, N., Chenard, Y., Subramanian, S., Brunet, M.-E., Stanley, J. (2025). Attack What Matters: Integrating Expert Insight and Automation in Threat-Model-Aligned Red Teaming. Now AI Conference, Santa Clara, CA, November 5.
- Gill, N., Montgomery, K. (2024). Interpretability for Generative AI. H2O GenAI Day, Atlanta, GA, January 23.
- Gill, N. (2023). Guardrails for LLMs. H2O Open Source GenAI World, San Francisco, CA, November 7.
- Gill, N., Mathur, A. (2022). Incorporating AI Governance to Increase Adoption in Business Applications. MLOps World 2022, New York, NY, July 14.
- Gill, N., Tanco, M. (2021). Security Audits for Machine Learning Attacks. MLOps World 2021, June 16.
- Gill, N. (2021). Training Understandable, Fair, Trustable and Accurate Predictive Modeling Systems. Duke Machine Learning Day, Durham, North Carolina, March 27.
- Gill, N. (2019). Human Centered Machine Learning. Artificial Intelligence Conference, San Jose, CA, September 11.
- Gill, N. (2019). Interpretable Machine Learning Using rsparkling. Symposium on Data Science and Statistics, Bellevue, Washington, May 31.
- Gill, N. (2019). Practical Machine Learning Interpretability Techniques. GPU Technology Conference, San Jose, CA, March 21.
- Gill, N. (2018). Distributed Machine Learning with H2O. Joint Statistical Meeting, Vancouver, Canada, August 1.
- Gill, N. (2018). H2O AutoML. Symposium on Data Science and Statistics, Reston, Virginia, May 16.
- Hall, P., Gill, N., Chan, M. (2018). Practical Techniques for Interpreting Machine Learning Models: Introductory Open Source Examples using Python, H2O and XGBoost. 1st ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, New York City, February 23-24.
- Gill, N., Hall, P., Chan, M. (2017). Driverless AI Hands-On Focused on Machine Learning Interpretability. H2O World, Mountain View, CA, December 11.
- Gill, N. (2017). From R Script to Production using rsparkling. Spark Summit, San Francisco, CA, June 14.
- Gill, N. (2016). Scalable Machine Learning in R with H2O. useR Conference, Stanford, Palo Alto, CA, July 11.
- Voytek, B., Porat, S., Chamberlain, J., Balthazor, J., Greenberg, Z., Gill, N., Gazzaley, A. (2013). Examining the efficacy of the iPad and Xbox Kinect for cognitive science research. 2nd Annual Meeting of the Entertainment Software and Cognitive Neurotherapeutics Society, Los Angeles, California, March 15-17.
- Greenberg, Z., Gill, N., Porat, S., Samaha, J., Kader, T., Voytek, B., & Gazzaley, A. (2013). Increased visual cortical noise decreases cued visual attention distribution. 20th Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Neuroscience Society, San Francisco, California, April 13-16.
- Tyler, C.W., Gill, N., & Nicholas, S. (2012). Hysteresis in Stereoscopic Surface Interpolation: A New Paradigm. 12th Annual Meeting of the Vision Sciences Society, Naples, Florida, May 11-16.
- Gill, N., Fencsik, D. (2012). Effects of Disruptions on Multiple Object Tracking. California Cognitive Science Conference, UC Berkeley, California, April 28.
- Gill, N., Fencsik, D. (2011). Effects of Distractions on Recovery Time. Psychology Undergraduate Research Conference, UC Berkeley, California, May 1.
Patents
- Chan, M., Gill, N., & Hall, P. (2024). Model Interpretation. U.S. Patent No. 11,922,283. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
- Chan, M., Gill, N., & Hall, P. (2022). Model Interpretation. U.S. Patent No. 11,386,342. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.